1213 今日总结

今日工作
- 使用 matrix 的坑:
原本我使用正则的方式去获取 transform 的 translateX, translateY, rotate, scale 参数
js
const img = document.querySelector('#img')
const styleStr = img.style.transform;
const patt = /正则匹配/
const value = styleStr.match(patt)但是这种方式获取,translateX, translateY, scale 都是很好用的,唯一 rotate 的获取很麻烦,远远不如 rotate(30deg) 这种方式直白
看操作:
js
const transformAttr = document.getComputedStyle(dom).transform; // 返回 matrix 数组
// matrix( a, b, c, d, e, f )
// matrix(scale, skew, rotate角度, scale, translateX, translateY)
// 这里的 rotate 不能直接获取,需要进行 sin, cos 进行计算才能得到;
// matrix(cosθ, sinθ, -sinθ, cosθ, 0, 0)
// x' = xcosθ- ysinθ + 0 = xcosθ-ysinθ
// y' = xsinθ + ycosθ + 0 = xsinθ+ycosθ总而言之:
如果是为了获取 rotate 属性,还不如直接使用正则的方式方便快捷,但是,需要注意的是 dom.style.transform 的属性只能在 style 设置,类 里面的,此方法无法获取到;
读读 张鑫旭 老师的文章学习学习
手撕代码
防抖节流等各种手写,http和网络,浏览器原理,性能优化,Webpack
选择排序-菜鸟教程-算法系列结合动图和例子学习
- 选择排序
首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置。
再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾。
重复第二步,直到所有元素均排序完毕。
算法复杂度:O(n²)
js
function selectionSort(arr) {
var len = arr.length;
var minIndex, temp;
for (var i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
minIndex = i;
for (var j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { // 寻找最小的数
minIndex = j; // 将最小数的索引保存
}
}
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
return arr;
}
selectionSort([5,4,3,2,1,8]) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8]- 快速排序:
参考:快速排序
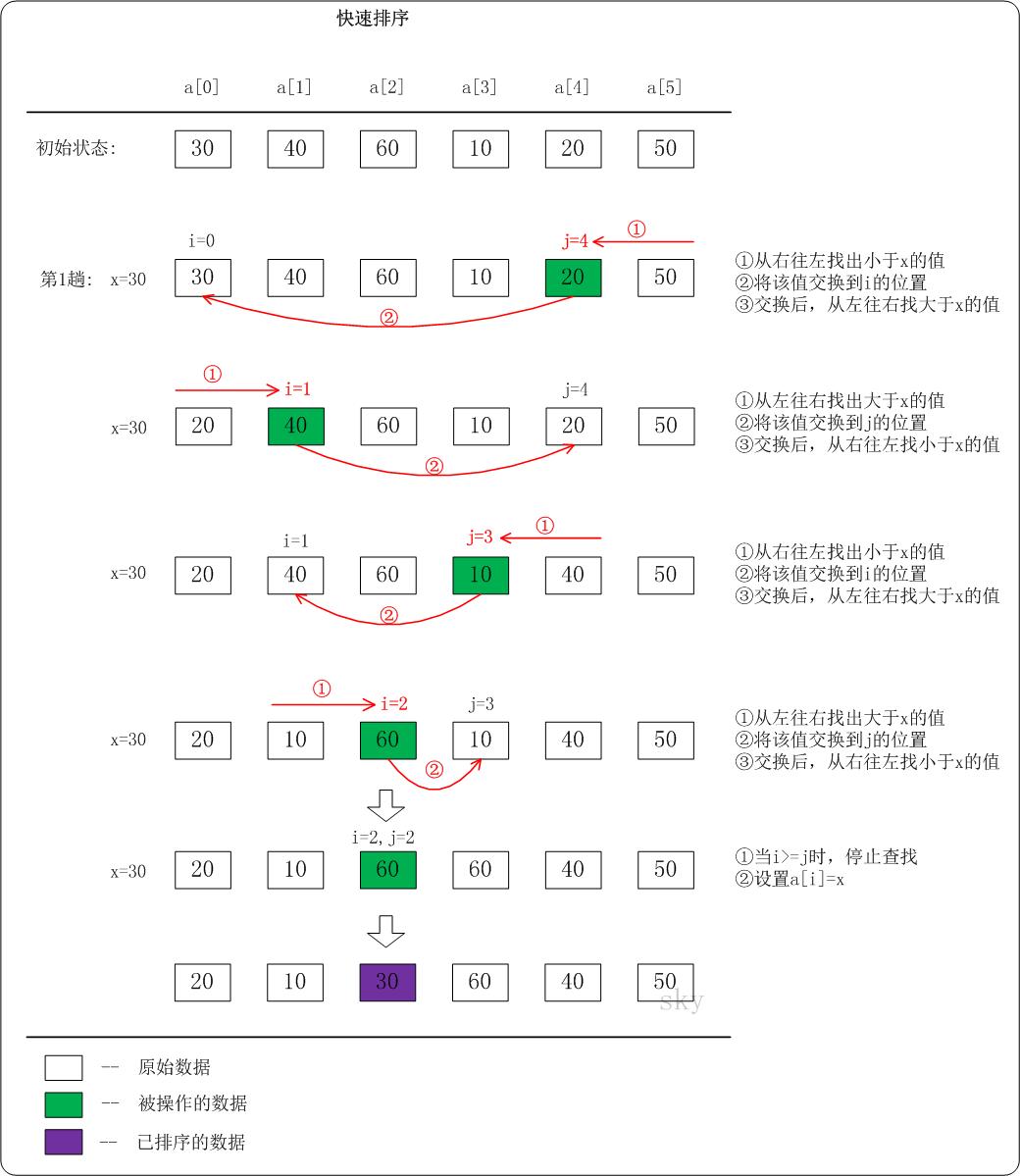
js
function quickSort(arr, l = 0, r = arr.length -1) {
if (l < r) {
let i, j, x;
i = l,
j = r,
x = arr[i];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && arr[j] > x) {
j-- // 从右向左找第一个小于x的数
}
if (i < j) {
arr[i ++] = arr[j]
}
while (i < j && arr[i] < x) {
i++ // 从左向右找第一个大于x的数
}
if (i < j) {
arr[j--] = arr[i]
}
}
arr[i] = x;
quickSort(arr, l, i-1) // 递归
quickSort(arr, i+1, r) // 递归
}
return arr
}
quickSort([5,4,3,2,1,8])