并查集算法思想
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sy4y1q79M?p=74
基础版本
本质:找 root 节点
2个方法:
- union:合并2 个元素,同一个根节点
- find:找到某个元素的根节点
使用:
union(x, y)
find(x)
特点:模板化,基本题目都是套用同一个模板
理解:
生活中的例子:
- A司令——军长——团长A1-团长A2——士兵
- B司令——军长——团长B1-团长B2——士兵
合并后,只有一个司令,其他都是下属
常用工具:
- 数组:root - 索引
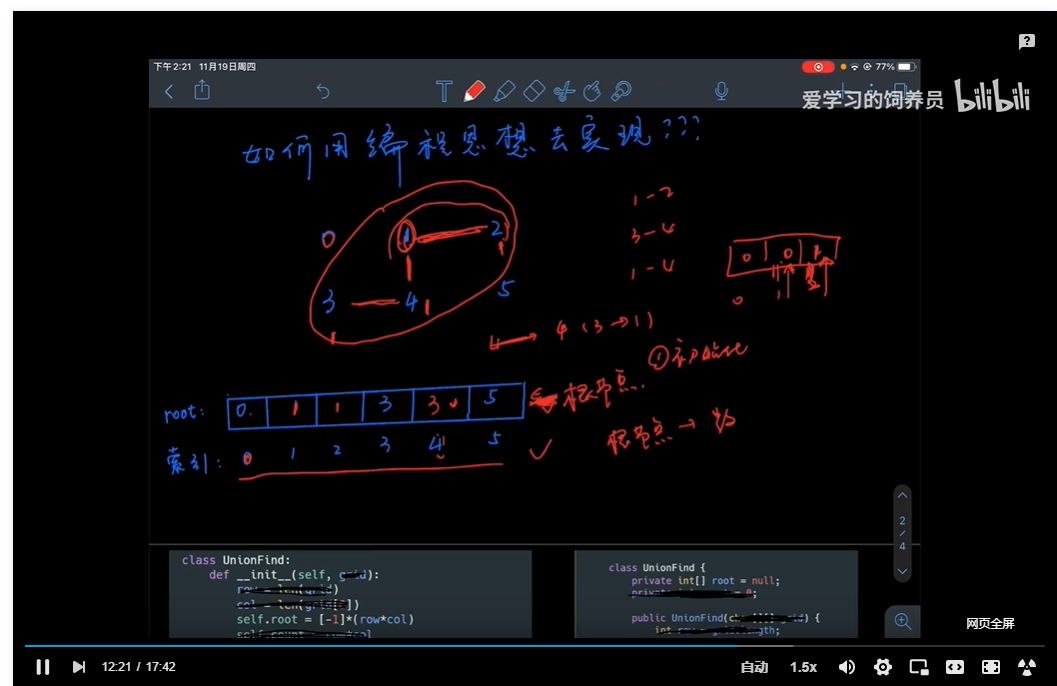
模板整理理解:
// 并查集模板
class UniFind {
root = []
count = 0
constructor(grid = [[]]) {
const row = grid.length
const col = grid[0].length
this.count = row * col
this.root = new Array(this.count)
for (let i=0; i< this.count; i++) {
this.root[i] = i
}
}
// 递归找 root 索引
find(x) {
if (x === this.root[x]) {
return x
}
//return this.root[x] = this.find(this.root[x])
return this.root[x]
}
// 同化操作
union(x = 0, y = 0) {
const rootX = this.find(x)
const rootY = this.find(y)
if (rootX !== rootY) {
this.root[rootX] = rootY
this.count -= 1
}
}
getCount() {
return this.count
}
}
练习题:
- 200 岛屿数量
- 547 省份数量
进阶版本
- find——> quickFind
快速找到 根节点 root:每次递归后,更改原来错误的 root,方便下一次查找
// 递归找 root 索引
find(x) {
if (x === this.root[x]) {
return x
}
// return this.root[x]
return this.root[x] = this.find(this.root[x])
}
- 路径压缩:权重法
例子:
2 棵不同高度的树合并,不是随意的直接合并,而是将 改动少的方案作为最有选择:高度少的树改动,高度多的不动。
题型一
难度中等
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
输出:1
示例 2:
输入:grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
输出:3
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300grid[i][j]的值为'0'或'1'
- 视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sy4y1q79M?p=69
- 题解:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/it_asGIDqQBoOrzdL1j2CQ
- 代码:
var numIslands = function(grid) {
if (grid === null || !grid.length) return 0
let result = 0
// 行数
const row = grid.length
// 列数
const col = grid[0].length
let waters = 0
const uf = new UniFind(grid)
for (let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '0') {
waters++;
} else {
const directions = [[0,1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]];
for (let dir of directions) {
const x = i + dir[0];
const y = j + dir[1];
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < row && y < col && grid[x][y] == '1') {
uf.union(x*col+y, i*col+j);
}
}
}
}
}
return uf.getCount() - waters;
}
class UniFind {
root = []
count = 0
constructor(grid = [[]]) {
const row = grid.length
const col = grid[0].length
this.count = row * col
this.root = new Array(this.count)
for (let i=0; i< this.count; i++) {
this.root[i] = i
}
}
find(x) {
if (x === this.root[x]) {
return x
}
return this.root[x] = this.find(this.root[x])
}
union(x = 0, y = 0) {
const rootX = this.find(x)
const rootY = this.find(y)
if (rootX !== rootY) {
this.root[rootX] = rootY
this.count -= 1
}
}
getCount() {
return this.count
}
}
难度中等
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
示例 1:
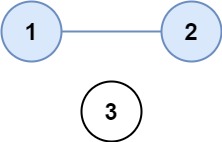
输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]
输出:2
示例 2:
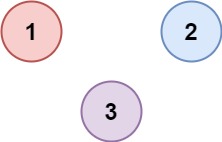
输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
输出:3
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j]为1或0isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
- 视频:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-provinces/solution/sheng-fen-shu-liang-by-leetcode-solution-eyk0/
- 题解:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-provinces/solution/sheng-fen-shu-liang-by-leetcode-solution-eyk0/
参考leetcode 官方题解
- 方法1:并查集法
Code:
var findCircleNum = function(isConnected) {
const provinces = isConnected.length;
const parent = new Array(provinces).fill(0).map((_, index) => index);
for (let i = 0; i < provinces; i++) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < provinces; j++) {
if (isConnected[i][j] == 1) {
// 找到城市,则为 父子关系
union(parent, i, j);
}
}
}
let circles = 0;
// union 完成以后,只有 father-城市 的 index 和 element 值 是相等的,因此只要遍历出 值即可
parent.forEach((element, index) => {
if (element === index) {
circles++;
}
});
return circles;
};
// 并操作
const union = (parent, index1, index2) => {
parent[find(parent, index1)] = find(parent, index2);
}
// 查操作
const find = (parent, index) => {
// 若没找到,则改变经过路径的 父节点值
if (parent[index] !== index) {
parent[index] = find(parent, parent[index]);
}
// 若找到,直接返回
return parent[index];
}
- 方法2:DFS
var findCircleNum = function(isConnected) {
const provinces = isConnected.length;
const visited = new Set();
let circles = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < provinces; i++) {
if (!visited.has(i)) {
dfs(isConnected, visited, provinces, i);
circles++;
}
}
return circles;
};
const dfs = (isConnected, visited, provinces, i) => {
for (let j = 0; j < provinces; j++) {
if (isConnected[i][j] == 1 && !visited.has(j)) {
visited.add(j);
dfs(isConnected, visited, provinces, j);
}
}
};