核心思想:不撞南墙不回头,一条路走到底;
DFS 和 回溯算法的区别:
- 回溯:DFS + 剪枝,按条件走,比如从2 开始,那么到 3 的时候,则不会再从 1 开始
例题:
- 78 子集
- 938 二叉搜索树的范围和
- 200 岛屿数量(说明:超级经典的题目)
题型一
难度中等
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[[],[0]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有元素 互不相同
- 方法:
- 题解:
- 说明:
- 代码:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var subsets = function(nums) {
const result = []
dfs(nums, result, 0, [])
return result
};
function dfs (nums, result, index, sub) {
result.push([].concat(sub))
if (nums.length === index) return
for (let i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
sub.push(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, result, i+1, sub);
sub.pop()
}
}
难度简单163收藏分享切换为英文接收动态反馈
给定二叉搜索树的根结点 root,返回值位于范围 [low, high] 之间的所有结点的值的和。
示例 1:
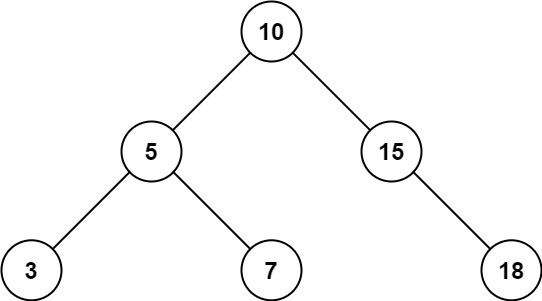
输入:root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15
输出:32
示例 2:
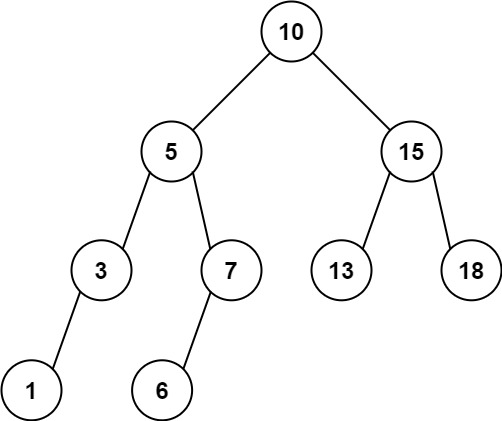
输入:root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10
输出:23
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 2 * 104]内 1 <= Node.val <= 1051 <= low <= high <= 105- 所有
Node.val互不相同
DFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} low
* @param {number} high
* @return {number}
*/
var rangeSumBST = function(root, low, high) {
if (!root) return 0
let total = 0
const leftSum = rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high)
const rightSum = rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high)
total = leftSum + rightSum
if (root.val >= low && root.val <= high) total += root.val
return total
};
- BFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} low
* @param {number} high
* @return {number}
*/
var rangeSumBST = function(root, low, high) {
if (!root) return 0
const queue = []
let result = 0
queue.push(root)
while(queue.length) {
let len = queue.length
while(len) {
const cur = queue.shift()
if (cur.val >= low && cur.val <= high) result += cur.val
if (cur.left) queue.push(cur.left)
if (cur.right) queue.push(cur.right)
len -= 1
}
}
return result
};
难度中等
给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
输出:1
示例 2:
输入:grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
输出:3
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300grid[i][j]的值为'0'或'1'
视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1sy4y1q79M?p=69&spm_id_from=pageDriver
题解:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/it_asGIDqQBoOrzdL1j2CQ
- DFS
/**
* @param {character[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
var numIslands = function(grid) {
if (grid === null || !grid.length) return 0
let result = 0
// 行数
const row = grid.length
// 列数
const col = grid[0].length
for (let i=0; i< row; i++) {
for (let j=0; j<col; j++) {
// 遇到 "1" 就换成 0 ,岛屿 +1,同时 【感染】周围 4 个点都为 "0"
if (grid[i][j] === "1") {
result += 1
dfs(grid, i, j, row, col)
}
}
}
return result
};
function dfs(grid, x, y, row, col) {
if (x < 0 || y < 0 || x >= row || y >= col || grid[x][y] === "0") return
grid[x][y] = "0"
// 四个方向上的点
dfs(grid, x + 1, y, row, col)
dfs(grid, x - 1, y, row, col)
dfs(grid, x, y + 1, row, col)
dfs(grid, x, y - 1, row, col)
}
- BFS + queue
var numIslands = function(grid) {
if (grid === null || !grid.length) return 0
let result = 0
let que = []
// 行数
const row = grid.length
// 列数
const col = grid[0].length
for (let i=0; i< row; i++) {
for (let j=0; j<col; j++) {
// 遇到 "1" 就换成 0 ,岛屿 +1,同时 【感染】周围 4 个点都为 "0"
if (grid[i][j] === "1") {
result += 1
// 将该坐标存入 队列
que.push([i, j])
grid[i][j] = "0"
while(que.length) {
let cur = que.shift()
let x = cur[0]
let y = cur[1]
// 上方位置的元素
if (x-1 >= 0 && grid[x-1][y] == '1' ) {
// 把坐标加进去
que.push([x-1, y]);
grid[x-1][y] = '0';
}
if (y-1 >= 0 && grid[x][y-1] == '1') {
que.push([x, y-1]);
grid[x][y-1] = '0';
}
if (x+1 < row && grid[x+1][y] == '1') {
que.push([x+1, y]);
grid[x+1][y] = '0';
}
if (y+1 < col && grid[x][y+1] == '1') {
que.push([x, y+1]);
grid[x][y+1] = '0';
}
}
}
}
}
return result
};
- 并查集
前置知识:并查集,作用 找到共同的祖先
- Union(x, y):合并 x, y 为同一个祖先
- Find(x):找到 x 的祖先: x = root[x]
前置知识:二维数组转换成一维数组
Eg:
var arr = [
[0,1,2, 3],
[4,5,6, 7],
[8,9,10,11],
[12,13,14,15],
]
坐标换算:
(1,2) ==> col: 1*4 + 2 = 6 ==> 公式:x * col + y
换成一维数组后的数字 7 所在位置:
locate(7) ==> x: x = 7 / 4 ==> 1
locate(7) ==> y: y = 7 % 4 ==> 3
===> locate(7) === (1, 3)
Code:
var numIslands = function(grid) {
if (grid === null || !grid.length) return 0
let result = 0
// 行数
const row = grid.length
// 列数
const col = grid[0].length
let waters = 0
const uf = new UniFind(grid)
for (let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '0') {
waters++;
} else {
const directions = [[0,1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]];
for (let dir of directions) {
const x = i + dir[0];
const y = j + dir[1];
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < row && y < col && grid[x][y] == '1') {
uf.union(x*col+y, i*col+j);
}
}
}
}
}
console.log('this.getCount', uf.getCount())
console.log('waters', waters)
return uf.getCount() - waters;
}
// 并查集模板
class UniFind {
root = []
count = 0
constructor(grid = [[]]) {
const row = grid.length
const col = grid[0].length
this.count = row * col
this.root = new Array(this.count)
for (let i=0; i< this.count; i++) {
this.root[i] = i
}
}
find(x) {
if (x === this.root[x]) {
return x
}
return this.root[x] = this.find(this.root[x])
}
// 同化操作
union(x = 0, y = 0) {
const rootX = this.find(x)
const rootY = this.find(y)
if (rootX !== rootY) {
this.root[rootX] = rootY
this.count -= 1
}
}
getCount() {
return this.count
}
}
针对 200 题这种题型 使用 并查集 方法做题的模板:
// 并查集模板
class UniFind {
root = []
count = 0
constructor(grid = [[]]) {
const row = grid.length
const col = grid[0].length
this.count = row * col
this.root = new Array(this.count)
for (let i=0; i< this.count; i++) {
this.root[i] = i
}
}
find(x) {
if (x === this.root[x]) {
return x
}
return this.root[x] = this.find(this.root[x])
}
// 同化操作
union(x = 0, y = 0) {
const rootX = this.find(x)
const rootY = this.find(y)
if (rootX !== rootY) {
this.root[rootX] = rootY
this.count -= 1
}
}
getCount() {
return this.count
}
}